what happens to a patient with a-fib to their bp if their heart rate goes up?
Overview
The Normal Eye Rhythm
The heart pumps blood to the rest of the torso. During each heart beat, the two upper chambers of the heart (atria) contract, followed by the two lower chambers (ventricles). These actions, when timed perfectly, let for an efficient pump. The timing of the heart'southward contractions is directed by the middle's electrical system.
The electrical impulse begins in the sinoatrial (SA node), located in the right atrium. Normally, the SA node adjusts the charge per unit of impulses, depending on the person'south activeness. For example, the SA node increases the charge per unit of impulses during exercise and decreases the rate of impulses during sleep.
When the SA node fires an impulse, electrical activity spreads through the right and left atria, causing them to contract and strength blood into the ventricles.
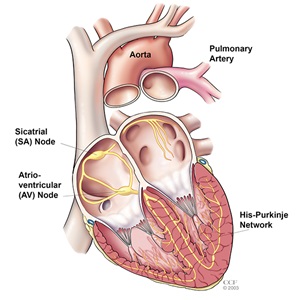
The impulse travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, located in the septum (near the eye of the heart). The AV node is the but electrical bridge that allows the impulses to travel from the atria to the ventricles. The impulse travels through the walls of the ventricles, causing them to contract. They squeeze and pump claret out of the middle. The correct ventricle pumps blood to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood to the torso.
When the SA node is directing the electric activity of the middle, the rhythm is chosen "normal sinus rhythm." The normal middle beats in this type of regular rhythm, about 60 to 100 times per infinitesimal at remainder.
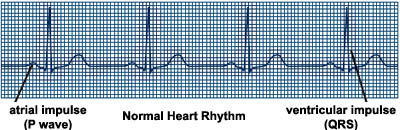
ECG recording of normal heart rhythm
What is atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast, cluttered rhythm in the atria. Because the electric impulses are so fast and chaotic, the atria cannot contract and/or squeeze blood effectively into the ventricle.
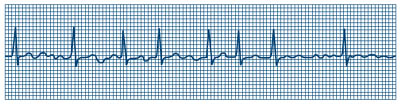
An ECG recording of atrial fibrillation
Instead of the impulse traveling in an orderly fashion through the heart, many impulses brainstorm at the same time and spread through the atria, competing for a chance to travel through the AV node. The AV node limits the number of impulses that travel to the ventricles, simply many impulses get through in a fast and disorganized manner. The ventricles contract irregularly, leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat. The rate of impulses in the atria can range from 300 to 600 beats per minute.
There are two types of atrial fibrillation. Paroxysmal is intermittent, meaning it comes and goes and continuous is persistent.
What are the dangers of atrial fibrillation?
Some people alive for years with atrial fibrillation without problems. However, atrial fibrillation tin pb to future issues:
- Considering the atria are beating speedily and irregularly, blood does non menstruum through them every bit rapidly. This makes the blood more likely to clot. If a clot is pumped out of the eye, it can travel to the brain, resulting in a stroke, or to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. People with atrial fibrillation are 5 to 7 times more likely to have a stroke than the full general population. Clots can also travel to other parts of the body (kidneys, heart, intestines), and cause other damage.
- Atrial fibrillation can decrease the center's pumping ability. The irregularity can make the heart work less efficiently. In addition, atrial fibrillation that occurs over a long period of time tin significantly weaken the heart and atomic number 82 to heart failure.
- Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased adventure of stroke, heart failure and even death.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes atrial fibrillation?
In that location is no one "crusade" of atrial fibrillation, although it is associated with many weather condition, including:
Most common causes
- After center surgery
- Cardiomyopathy
- Chronic lung disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Coronary artery disease
- Eye failure
- Center valve disease
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Pulmonary hypertension
Less common causes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pericarditis
- Viral infection
In at least ten percent of the cases, no underlying centre disease is found. In these cases, AF may be related to alcohol or excessive caffeine use, stress, sure drugs, electrolyte or metabolic imbalances, severe infections, or genetic factors. In some cases, no cause can exist establish.
The adventure of AF increases with age, peculiarly after age 60.
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
You may have atrial fibrillation without having any symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include:
- Middle palpitations - Sudden pounding, fluttering or racing awareness in the breast
- Lack of energy or feeling over-tired
- Dizziness - Feeling calorie-free-headed or faint
- Chest discomfort - Pain, pressure level or discomfort in the chest
- Shortness of breath - Having difficulty breathing during normal activities and even at residual
Diagnosis and Tests
How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed?
The most ordinarily used tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The ECG draws a moving picture on graph paper of the electric impulses traveling through the heart muscle. An EKG provides an electrical "snapshot" of the heart.
- For people who accept symptoms that come and go, a special monitor may need to be used to "capture" the arrhythmia.
- Holter monitor: A minor external recorder is worn over a brusque period of time, ordinarily one to three days. Electrodes (sticky patches) are placed on the skin of your chest. Wires are attached from the electrodes to the monitor. The electrical impulses are continuously recorded and stored in the monitor. Afterwards the monitor is removed, a technician uses a calculator to analyze the information to evaluate the heart's rhythm.
- Portable issue monitor: A monitor that is worn for about a calendar month for patients who take less frequent irregular heartbeat episodes and symptoms. Electrodes (sticky patches) are placed on the skin of your breast. Wires are attached from the electrodes to the monitor. The patient presses a push to actuate the monitor when symptoms occur. The device records the electrical activeness of the heart for several seconds. The patient then transmits the device's recorded information over a phone line to the doctor's function for evaluation. The portable consequence monitor is very useful in determining what heart rhythm is causing your symptoms.
- Transtelephonic monitor: When y'all develop symptoms of atrial fibrillation, a strip of your current heart rhythm tin can be transmitted to your doctor's office over the telephone, using a monitor with ii bracelets or by placing the monitor confronting your breast wall.
These monitoring devices help your medico determine if an irregular eye rhythm (arrhythmia) is causing your symptoms. Larn more about diagnostic tests.
Management and Handling
How is atrial fibrillation treated?
The goals of handling for atrial fibrillation include regaining a normal heart rhythm (sinus rhythm), controlling the center rate, preventing claret clots and reducing the risk of stroke.
Many options are bachelor to treat atrial fibrillation, including lifestyle changes, medications, catheter-based procedures and surgery. The type of treatment that is recommended for you is based on your eye rhythm and symptoms.
Medications
Initially, medications, are used to treat atrial fibrillation. Medications may include:
Rhythm control medications (antiarrhythmic drugs)
Antiarrhythmic medications help render the eye to its normal sinus rhythm or maintain normal sinus rhythm.
There are several types of rhythm control medications, including: procainamide (Pronestyl); disopyramide (Norpace); flecainide acetate (Tambocor); propafenone (Rythmol); sotalol (Betapace); dofetilide (Tikosyn) and amiodarone (Cordarone).
Yous may have to stay in the hospital when you lot first start taking these medications and then your middle rhythm and response to the medication tin exist carefully monitored. These medications are effective 30 to lx percent of the time, just may lose their effectiveness over time. Your doctor may need to prescribe several different antiarrhythmic medications to determine the right i for y'all.
Some rhythm control medications may actually crusade more arrhythmias, so it is important to talk to your doctor nigh your symptoms and any changes in your status.
Rate control medications
Rate control medications, such as digoxin (Lanoxin), beta-blockers [metoprolol (Toprol, Lopressor)], and calcium aqueduct blockers such as verapamil (Calan) or diltiazem (Cardizem), are used to assist irksome the center rate during atrial fibrillation. These medications practice non control the heart rhythm, only do forbid the ventricles from beating too rapidly.
Anticoagulant medications
Anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy medications, such every bit warfarin (Coumadin), warfarin alternatives, or aspirin reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke, but they practise non eliminate the risk. Regular blood tests are required when taking Coumadin to evaluated the effectiveness. If you are taking warfarin alternatives, regular blood tests are not required. Talk to your doctor about the anticoagulant medication that is correct for you.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to taking medications, at that place are some changes you can brand to ameliorate your centre wellness.
- If your irregular heart rhythm occurs more than often with certain activities, avoid those activities and tell your doctor. Sometimes, your medications may demand to be adjusted.
- Quit smoking.
- Limit your intake of alcohol. Moderation is the central. Ask your dr. for specific alcohol guidelines.
- Limit the employ of caffeine. Some people are sensitive to caffeine and may notice more than symptoms when using caffeinated products (such as tea, coffee, energy drinks, colas and some over-the-counter medications).
- Beware of stimulants used in cough and cold medications, as some of these medications incorporate ingredients that may increase the hazard of irregular centre rhythms. Read medication labels and ask your doctor or chemist what blazon of cold medication is best for y'all.
- Control high claret pressure.
- If you are obese or overweight, achieve a desirable weight.
- Control blood sugar levels.
- Care for sleep apnea.
Procedures
When medications practise not work to correct or command atrial fibrillation, or when medications are not tolerated, a process may be necessary to treat the abnormal middle rhythm, such as: electric cardioversion, pulmonary vein antrum isolation procedure, ablation of the AV node followed by pacemaker placement, or surgical ablation (Maze procedure or minimally invasive surgical treatment).
- Electrical Cardioversion : A cardioversion electrically "resets" the heart. Medications lone are non ever constructive in converting atrial fibrillation to a more normal rhythm. Sometimes cardioversion is used to restore a normal heart rhythm and allow the medication to successfully maintain the normal rhythm. Cardioversion oftentimes restores a normal rhythm, although its issue may not be permanent. After a short-acting anesthesia is given that puts the patient to sleep, an electrical shock is delivered through patches placed on the chest wall. This shock will synchronize the heartbeat and restore a normal rhythm.
- Pulmonary Vein Ablation : Pulmonary vein ablation (also chosen pulmonary vein antrum isolation or PVAI) may be an choice for people who cannot tolerate medications or when medications are not effective in treating atrial fibrillations.
- Because atrial fibrillation ordinarily begins in the pulmonary veins or at their attachment to the left atrium, free energy is practical around the connections of the pulmonary veins to the left atrium during the pulmonary vein ablation procedure.
- Ablation of the AV node: During this type of ablation, catheters are inserted through the veins (usually in the groin) and guided to the heart. Radiofrequency energy is delivered through the catheter to sever or injure the AV node. This prevents the electrical signals of the atrium from reaching the ventricle. This result is permanent, and therefore, the patient needs a permanent pacemaker to maintain an adequate heart charge per unit. Although this procedure can reduce atrial fibrillation symptoms, it does not cure the condition. Considering the patient will proceed to have atrial fibrillation, an anticoagulant medication is prescribed to reduce the run a risk of stroke.
- Important note: Due to improve handling alternatives, AV node ablation is rarely used to treat atrial fibrillation.
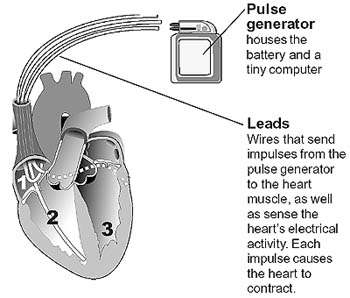
Device Therapy
Permanent Pacemaker : A pacemaker is a device that sends small electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable middle rate. Pacemakers are implanted in people with AF who have a dull center rate. The pacemaker has a pulse generator (that houses the battery and a tiny computer) and leads (wires) that send impulses from the pulse generator to the heart musculus, besides as sense the heart's electrical activity.
Newer pacemakers have many sophisticated features, designed to help with the management of arrhythmias and to optimize heart rate-related function equally much as possible.
Left Atrial Appendage Closure
The left atrial bagginess (LAA) is a small, ear-shaped sac in the muscle wall of the left atrium (top left bedchamber of the heart). It is unclear what function, if whatsoever, the LAA performs. When a patient has atrial fibrillation, the electrical impulses that control the heartbeat practise not travel in an orderly mode through the heart. Instead, many impulses brainstorm at the aforementioned time and spread through the atria. The fast and chaotic impulses do not requite the atria fourth dimension to contract and/or effectively squeeze blood into the ventricles. Considering the LAA is a fiddling pouch, blood collects at that place and can form clots in the LAA and atria. When blood clots are pumped out of the heart, they tin can cause a stroke. People with atrial fibrillation are 5 to 7 times more likely to have a stroke than the general population.
If you are at hazard of developing clots in the left atrium/LAA, your dr. may recommend a procedure to seal off your LAA. This can reduce your gamble of stroke and eliminate the need to take blood-thinning medication.There are several options and devices available for closure of the LAA, such as the WATCHMAN device. Your doctor will talk to you nearly the best options for your individual needs.
Surgical Treatment
Sure patients are candidates for surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. These include patients with i or more of the following characteristics:
- Atrial fibrillation that persists after optimal treatment with medications
- Unsuccessful catheter ablation
- Blood clots in the left atrium
- History of stroke
- Enlarged left atrium
- Other atmospheric condition requiring heart surgery
Maze procedure: During this process, a series of precise incisions or lesions are fabricated in the right and left atria to confine the electrical impulses to divers pathways to achieve the AV node. These incisions prevent the abnormal impulses from affecting the atria and causing atrial fibrillation.
The surgical Maze procedure tin be performed traditionally with a technique in which precise surgical scars are created in the atria. It may also be performed using newer technologies designed to create lines of conduction block with radiofrequency, microwave, light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation, ultrasound or cryothermy (freezing). With these techniques, lesions and ultimately scar tissue is created to block the abnormal electrical impulses from existence conducted through the middle and to promote the normal conduction of impulses through the proper pathway.
Many of these approaches can be performed with minimally invasive (endoscopic or "keyhole") surgical techniques.
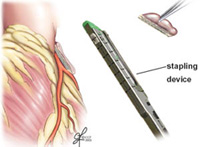
Excision of the Left Atrial Appendage
If a patient has atrial fibrillation and requires surgery to treat other heart issues (such as valve disease or coronary avenue disease), the surgeon may perform the surgical treatment for atrial fibrillation at the aforementioned time.
Excision or exclusion of the left atrial appendage: During surgical procedures to treat atrial fibrillation, the left atrial appendage is removed and the tissue is closed with a special stapling device, or information technology can be excluded with a device called the AtriClip. The AtriClip is implanted from outside the heart and stops the blood flow between the LAA and left atrium.
Resources
Eye for Atrial Fibrillation
Cleveland Dispensary'southward Eye for Atrial Fibrillation offers comprehensive treatment for patients with atrial fibrillation.Specialists from cardiology, cardiac surgery, cardiac imaging, arrhythmia inquiry, emergency medicine, neurology and geriatric medicine combine their expertise to tailor individual approaches for their patients.
When you come to Cleveland Clinic'south Center for Atrial Fibrillation, you will receive care from some of the leading specialists in the earth. Many of our physicians participate in the enquiry and development of the newest treatments.
Our physicians participate in scientific and clinical investigations focused on improving our understanding of the underlying causes of atrial fibrillation, in order to increase the long-term efficacy of available treatment options.
Doctors vary in quality due to differences in training and experience; hospitals differ in the number of services available. The more complex your medical problem, the greater these differences in quality become and the more they matter.
Clearly, the doctor and hospital that y'all choose for complex, specialized medical intendance will take a direct bear upon on how well you do. To assistance yous make this option, delight review our Miller Family Middle, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Outcomes.
Cleveland Clinic Center, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Cardiologists and Surgeons
Choosing a doctor to care for your aberrant heart rhythm depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with Arrhythmias:
- Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing: cardiology evaluation for medical management or electrophysiology procedures or devices - Call Cardiology Appointments at cost-free 800.223.2273, extension 4-6697 or request an appointment online.
- Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical handling for atrial fibrillation, epicardial lead placement, and in some cases if necessary, lead and device implantation and removal. For more information, please contact us.
- MyConsult Online Second Stance Service.
The Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Plant has specialized centers to care for certain populations of patients:
- Center for Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Prevention Center
- Ventricular Arrhythmia Eye
- Inherited Arrhythmia Clinic
Learn more about experts who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias in younger patients with aberrant heart rhythms:
- Visit The Centre for Pediatric and Congenital Middle Diseases spider web site
- Find a pediatric cardiologist
See About Us to learn more about the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Centre, Vascular & Thoracic Institute.
Contact
If you need more than information virtually PVCs or to make an appointment with a Cleveland Clinic heart specialist, click here to contact us, chat online with a nurse or call the Miller Family Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Found Resource & Information Nurse at 216.445.9288 or toll-complimentary at 866.289.6911. We would exist happy to help you.
Becoming a Patient
- Make an appointment
- Plan Your Visit
- Billing & Insurance
- Company Amenities
Treatment Options
- Arrhythmia Treatments
Treatment Guides
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- All Miller Family Center, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Handling Guides
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests are used to diagnose your abnormal heartbeat and the nigh effective treatment method.
- Diagnostic testing
Anatomy
- How the heart beats
- Your heart and claret vessels
Webchats
Our webchats and video chats give patients and visitors another opportunity to ask questions and interact with our physicians.
- Abnormal Center Rhythm webchats and video chats
- All Miller Family unit Centre, Vascular & Thoracic Institute webchats
Videos
- Heart Rhythm Disorders and Treatments Videos
- All Miller Family unit Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Videos
Interactive Tools
- Miller Family Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Constitute Interactive Tools
Resources Links
- Recovery at dwelling
- Back up Groups and Information
- Visit Health Essentials* - Read articles on rhythm disorders and healthy living on Health Essentials
- Follow Center, Vascular & Thoracic Found webchats and news stories on Twitter*
- Subscribe to Center, Vascular & Thoracic eNews
Why cull Cleveland Clinic for your intendance?
Our outcomes speak for themselves. Please review our facts and figures and if you take any questions don't hesitate to enquire.
matthiesthandsoll.blogspot.com
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16765-atrial-fibrillation-afib
0 Response to "what happens to a patient with a-fib to their bp if their heart rate goes up?"
Post a Comment